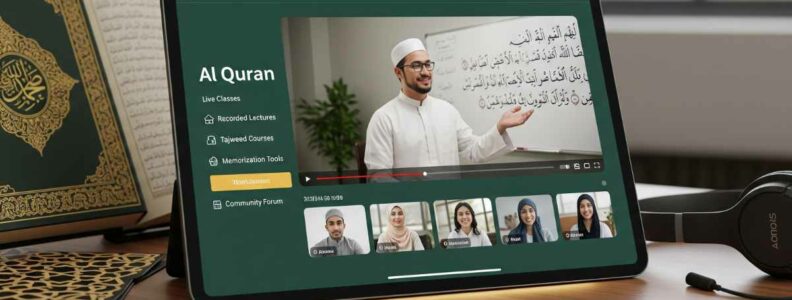
Learn Online Quran with Tajweed is perhaps the strongest method of connecting with the Quran these days. Tajweed is not mere rules of pronunciation. It is preserving the sacred words in their pristine beauty and meaning. These days, with online technologies, children, adults, and even working professionals can access expert teachers from home.
Having the ability to learn with flexibility, customized lessons, and gentle guiding makes online learning of Tajweed the absolute best option. Anyone can now perfect recitation with accuracy and yet deepen their spiritual connection with the Quran.
What is Tajweed and Why Does it Matter?
Learn Quran Online with Tajweed begins with understanding what Tajweed means. It refers to rules that guide recitation, ensuring letters are pronounced correctly and words flow as they should. Without Tajweed, words can be mispronounced, which may change the meaning. This makes Tajweed essential for preserving the Quran as it was revealed.
Learning Tajweed also connects believers spiritually to the Quran. Reciting with Tajweed creates a rhythm that touches the heart and soul. It is the way the Quran was first heard and passed on. This is why Muslims around the world seek teachers who can guide them in learning Tajweed properly.
Benefits of Learning Quran with Tajweed Online
The benefits of choosing to learn Quran online with Tajweed are many. First is accessibility. Students can attend classes from home at any time without traveling. Online lessons also provide one-on-one sessions, where teachers focus completely on the learner. This level of attention speeds up progress.
Affordability is another strong benefit. Online Tajweed classes usually cost less than traditional lessons. Many programs also give recorded sessions, making it easy to review and repeat lessons. The mix of live classes, recordings, and interactive tools creates an effective learning system for all ages.
Meet the Expert Teachers
To learn Quran online with Tajweed successfully, expert teachers play the most important role. Many online tutors are certified with Ijazah, meaning they have deep knowledge of Tajweed. They are trained to guide learners step by step with patience and care.
These teachers also speak different languages such as Arabic, Urdu, and English. This makes it easier for learners across the world to study in a language they understand. Whether a child, beginner, or advanced student, teachers adjust their style to make lessons engaging and supportive.
Flexible Online Quran Classes for All Ages
One reason many families choose to learn Quran online with Tajweed is flexibility. Students can pick times that fit their daily routine, whether in the morning, evening, or weekends. This makes online classes ideal for children, working adults, or families in different time zones.
Online Tajweed programs are designed for every level. Children often begin with basics, while adults may focus on fluency or advanced Tajweed. Some students also use this method for Hifz, or memorization. Flexibility makes it possible for every learner to grow at their own pace.
How Online Tajweed Classes Work
When you learn Quran online with Tajweed, the process is simple. Students first register on the platform and are matched with a teacher. Many schools offer a trial class to help students decide if the program fits their needs.
Classes usually happen through Zoom or Skype. Teachers listen to recitation, correct mistakes, and explain Tajweed rules step by step. Screen sharing, digital Qurans, and recordings make the lessons interactive. This hands-on approach ensures students stay engaged while learning properly.
Online vs. Traditional Tajweed Learning
Traditional Tajweed learning often means going to a mosque or madrasa. This can take extra time and limit the choice of teachers. Online learning removes these barriers. It provides a wider range of teachers and allows lessons to happen at home.
| Aspect | Online Tajweed Learning | Traditional Learning |
| Flexibility | High – choose own schedule | Fixed class times |
| Teacher Availability | Global certified teachers | Limited local teachers |
| Cost | Affordable and transparent | Travel and higher fees |
| Resources | Digital tools and recordings | Mostly books and oral |
| Comfort | Home-based learning | Travel required |
Tips to Succeed in Online Tajweed Learning
To truly benefit when you learn Quran online with Tajweed, consistency is key. Students should set a quiet learning space at home and attend every class with focus. Regular daily practice outside of lessons makes recitation stronger and more natural.
Another important tip is communication. Asking questions and seeking feedback from teachers helps fix mistakes early. Using Tajweed apps or listening to well-known reciters also supports faster learning. With discipline and regular effort, success in Tajweed becomes much easier.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While many students enjoy learning Tajweed online, challenges can appear. For children, staying focused may be difficult. Teachers solve this by keeping lessons short and interactive. Parents also help by creating a distraction-free environment.
Pronunciation is another challenge, especially for non-Arabic speakers. Teachers use repetition and recordings to help with this. Flexible schedules also solve the problem of time zone differences. Online systems are built to make sure students stay on track despite these issues.
Success Stories and Real Examples
Thousands of students now learn Quran online with Tajweed and have inspiring stories. One child in the UK who struggled with Arabic letters improved greatly after just three months of online Tajweed lessons. His parents noticed new confidence in his recitation.
Another example is a professional in Canada. Despite a busy career, she managed to complete a Tajweed course online within six months. She described the experience as life-changing. Her connection with the Quran grew stronger because of the flexible schedule and expert guidance.
Role of Technology in Tajweed Learning
Technology has changed the way Muslims around the world connect with the Quran. When you learn Quran online with Tajweed, you benefit from modern tools such as interactive apps, audio playback, and digital whiteboards. These tools make it easier to follow lessons step by step and correct mistakes quickly.
Teachers also use recordings to give students material for extra practice. This means learners can listen to their own recitation or compare it with expert reciters. The use of technology makes Tajweed lessons more engaging and ensures students never feel left behind.
Why Parents Prefer Online Tajweed Classes for Kids
Many parents today choose to learn Quran online with Tajweed for their children because it is safe and convenient. Kids can study from home without traveling to a madrasa or mosque. This saves time and allows parents to monitor progress closely.
Online teachers also use child-friendly methods to make classes fun. They include games, stories, and repetition, which keep young learners motivated. Parents find this system more reliable as they can directly communicate with teachers about their child’s improvement.
Certification and Progress Tracking
A big advantage of online programs is certification. Many platforms provide certificates when students finish their Tajweed courses. This recognition motivates learners to stay committed. Certificates also give parents peace of mind, knowing that their children are reaching real milestones.
Progress tracking is another helpful feature. Students can see how far they have come and what areas need improvement. When you learn Quran online with Tajweed, this step-by-step monitoring ensures steady growth in both knowledge and confidence.
Community and Global Connection
When you learn Quran online with Tajweed, you join a global community of learners. Students from different countries, cultures, and backgrounds share the same journey. This creates a sense of unity and strengthens bonds across the Muslim Ummah.
Online platforms often host group sessions or events where learners can connect. These gatherings allow students to share experiences, recite together, and inspire one another. The sense of belonging makes learning more enjoyable and meaningful.
How to Get Started
If you want to learn Quran online with Tajweed, the first step is simple registration. Most schools guide you through an easy sign-up process. After that, you either choose a teacher or get matched with one. A free trial class is usually offered.
Once lessons begin, students can select a package that fits their goals. Pricing is often clear, with different plans for individuals and families. Many platforms also allow cancellation at any time. This makes starting Tajweed learning online a safe and risk-free choice.
FAQs
Can children learn Tajweed online effectively?
Yes, online Tajweed programs are designed for children. Teachers use interactive methods that keep young learners engaged.
How long does it take to master Tajweed?
Basic Tajweed can be learned in a few months, but mastering advanced rules may take a year or more, depending on practice.
Do I need to know Arabic to start Tajweed classes?
No, many programs teach Tajweed from the very beginning and use the student’s own language for explanation.
What if I miss a class?
Most online schools allow rescheduling. Some also provide recordings so students can review missed lessons.
Are female teachers available for sisters?
Yes, many platforms have certified female teachers to ensure a comfortable learning experience for sisters and children.
Conclusion
Learn Quran Online with Tajweed is a powerful way to grow closer to the Quran. With certified teachers, flexible classes, and modern tools, anyone can learn accurate recitation from home. This method removes barriers of time, place, and cost, making Tajweed accessible for all. By practicing daily and staying committed, students can achieve both spiritual growth and accurate recitation. The time to begin is now, and online Tajweed learning makes it possible for every believer to master the words of Allah.